Get your cervical pain treated: Spine act physiotherapy clinic is one of the best physiotherapy clinic near pari chowk.
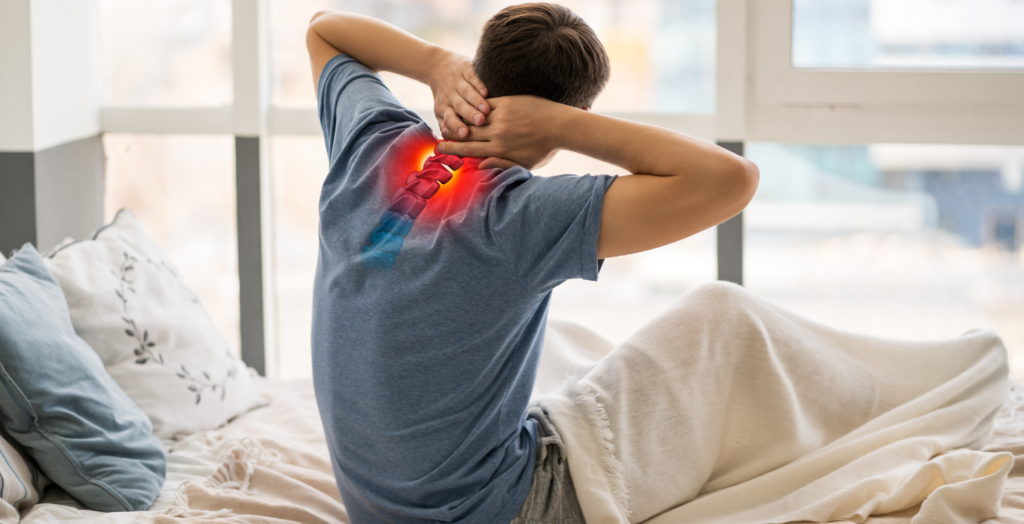

Cervical Radiculopathy treatment doctor near sector 148, Greater Noida
Neck pain is a prevalent issue that can cause significant pain and disability. Up to 40% of work absenteeism is due to individuals with a history of neck pain. Cervical radiculopathy occurs when a nerve root in the spine is compressed or impeded, leading to pain that can spread beyond the neck and into the arm, chest, shoulders, and upper back. Common signs of impingement include muscle weakness and impaired deep tendon reflexes. These deficits may worsen over time, leading to a decrease in quality of life and daily function. While most symptoms can be treated with supportive care, more severe signs of functional loss may require rehabilitation or surgery. For physical therapy, Dr. Yash Pratap is one of the best physio physiotherapist to treat spine and shoulder conditions.
Any condition that causes compression or irritation of a spinal nerve root can result in radicular symptoms. In younger patients, typically in the third and fourth decade, disc trauma and herniation are the most frequent causes of impingement with increasing age, the causation is degenerative. Disc degeneration is the most common cause in the fifth and sixth decades. In the seventh decade, causation stems from foraminal narrowing due to arthritic change.
How commonly is cervical radiculopathy found?
Cervical radiculopathies occur at an incidence rate of approximately 85 persons per 100,000. The C7 nerve root is most frequently impacted, with more than half of all cases affecting this level. Roughly a quarter of cases involve the C6 nerve root. Nerve roots C1 to C5 and C8 are less impacted. Risk factors for developing radicular disease include manual labor with heavy lifting, driving, or operating vibrating equipment. Chronic smoking history can increase the risk of radiculopathies.
Different Treatment options used by physiotherapists for complete cervical recovery :
Surgery or non-surgical treatment can be used to treat CR. In CR, there is some weak proof that surgery may help with pain faster than physical therapy or hard-collar immobilization, but in the long run, there is little to no difference. There may be a 4% chance of bad things happening after surgery. Because of this, conservative management is the best first step for most people with CR. However, they should be sent to a spine surgeon if their symptoms won’t go away after 6 weeks of nonoperative treatment, if they have a motor weakness that lasts longer than 6 weeks, if they are showing signs or symptoms of myelopathy, or if their spine is unstable or deformed. Because of this, research on conservative management is very important for learning about the first step in treating this problem.
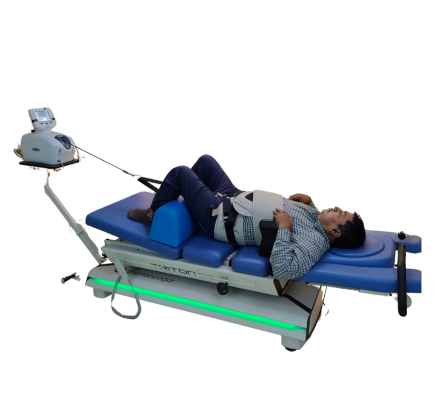
Vertebral body separation, facet joint movement, intervertebral foramen expansion, and soft tissue stretching are possible physiological effects of CT. The usefulness of cervical traction in conjunction with other physical treatment techniques in CR has not yet been assessed by a systematic review.
There are both invasive and noninvasive methods used in conservative treatment. Not as much evidence supports the success of acupuncture and injection therapy compared to invasive treatments. In a figio therapy session, they might use cervical traction, postural education, exercise, and manual therapy on the cervical and thoracic spine as part of noninvasive treatment. These many techniques are frequently applied in a multimodal therapeutic strategy. Cervical traction (CT) remains a commonly recommended treatment for patients with CR, and it is regularly utilized as a supplemental modality during outpatient rehabilitation. It can be applied sporadically or continuously, mechanically or manually. At our facility, Spineact we have one of the rarest advanced modalities Decompression Machine that helps the patients to recover faster.
When it comes to treating cervical radiculopathy, physiotherapy works well and often eliminates symptoms. Your physio therapist will use the results of your initial evaluation to create a personalized treatment plan for you. The following could be part of the pt therapy treatment plan:
Pain Control:
The area’s pain and inflammation are to be reduced as a priority. In the first 24 to 48 hours after the onset of pain, applying ice packs to the neck and scapular (shoulder blade) region can help reduce inflammation. After this amount of time, you can apply moist heat to help the surrounding muscles relax. To help your neck relax, your physical therapist can suggest wearing a soft cervical collar at certain points during the day. It can be advised that you use a cervical contoured pillow to support your neck correctly and improve your quality of sleep. Get your cervical pain treated by one of the best physiotherapists in greater noida – Dr. Yash Pratap.
Manual Therapy:
To relieve pressure in the cervical (neck) region, your physical therapist may employ manual treatment techniques including manual cervical traction. Radiating into the arm, this technique might offer instant relief from pain and numbness. The muscles of the cervical spine and scapular (shoulder blade) area can also be gently massaged. This method facilitates pain alleviation and healing by relaxing the muscles and increasing local circulation.

Education in Posture:
An essential component of therapy is posture teaching. To encourage proper posture and safeguard your neck, your physical therapist could advise making changes to your workspace and working habits. This can entail spending only 15 to 20 minutes seated at a time during the early phases of rehabilitation. Additionally, you will learn safe bending, reaching, and lifting techniques that save your spinal discs from unnecessary strain throughout the day.

Exercises for Range of Motion:
To help you regain normal mobility and reduce your discomfort, your physical therapist will teach you modest cervical mobility exercises. None of these workouts must exacerbate the pain that’s shooting down into your arm when you’re first recovering. It’s critical that you precisely describe your symptoms to your physio therapist. Your neck may stiffen if you spend a lot of your workweek seated at a desk. To help you become more mobile, your therapist will teach you stretches for your neck that relieve strain from prolonged sitting, at our clinic Spineact, people search for the best physiotherapy clinic near pari chowk and the best physiotherapy clinic for cervical in greater noida.

Strengthening Activities:
Your physical therapist will assist you in identifying the muscle groups that require strengthening of the specific spinal nerves that are implicated in your situation. Once your arm is pain-free, you can start doing more strenuous strengthening activities. There will also be neck stability (strengthening) exercises. Long after your formal physical therapy sessions are over, you will receive a home workout routine to maintain the strength in your neck, shoulder, arm, and upper back.
Practical Instruction
Your physiotherapist will assist you return to work, sports, and other daily activities by working on functional exercises as your symptoms become better. For instance, you will learn how to carry out tasks like overhead reaching, pushing, tugging, and extended sitting to prevent unnecessary strain on your neck.

Is it Possible to Prevent Cervical Radiculopathy Condition?
Your physical therapist will instruct you on the following strategies to avoid a recurrence of cervical radiculopathy:
- Preserving appropriate posture: Sitting at a desk or in the car requires good posture and the use of a supportive pillow.
- Arrange your workspace to reduce excessive pressure on the back. During the workplace, you could be recommended to use a hands-free phone or to adjust the monitor on your computer to prevent excessive neck twisting or stretching in repeating directions.
- Maintaining regular exercise can help to keep the flexibility and strength of the spinal muscles, which include the core, middle back, and upper body muscles.
- Maintaining an appropriate weight reduces needless strain on the back.
Other different treatment strategies used in pt therapy:
Treatment of cervical radiculopathy should be approached in a stepwise fashion. Also, while surgery can provide significant relief, there is little evidence that surgery provides a clear advantage over non-surgical treatment in an acute setting. Manual-based treatments, including traction, mobilization, and manipulation, are used for cervical radiculopathy rehabilitation. Traction is considered the main cornerstone based on available literature. In addition, manual therapy can include various forms of muscle active releases and exercises, including stretching, strengthening, and neurodynamic exercises. Mechanical traction provides improved outcomes compared to manual traction based on the limited research comparing the two, though further research is needed.
Therapeutic efforts are cited as having multiple benefits, including reducing pain, improving functional outcomes, and improving the timeliness of outcomes depending on the onset of treatment and how aggressive the treatment plan is. It is worth noting that the effectiveness of individual treatments has not been demonstrated in the literature. Combining these treatments has been shown to reduce radiculopathy symptoms. Intermittent cervical traction, immobilization, and ultrasound and infrared treatment. A recent study of these and eight other studies found that exercise regimens typically focused on strength training and stretching of the neck muscles. Additional considerations in designing a physical therapy program for radiculopathy include the patient’s general functional status (aerobic training if aerobic conditioning is suboptimal) and strength training of the neck and chest.
A well-designed physical therapy program should progress the patients through these stages as pain improves, beginning with gentle range of motion exercises, and adding strengthening and conditioning activities once the acute symptoms subside. Finally, pt therapy programs should include some components of postural and ergonomic training, In our one-month rehabilitation program for treating cervical radiculopathy we focus on a patient-centric approach, people search for good physiotherapists near me Japeey Greens.
